The rise of AI girlfriends — why your ex’s next girlfriend might be a chatbot
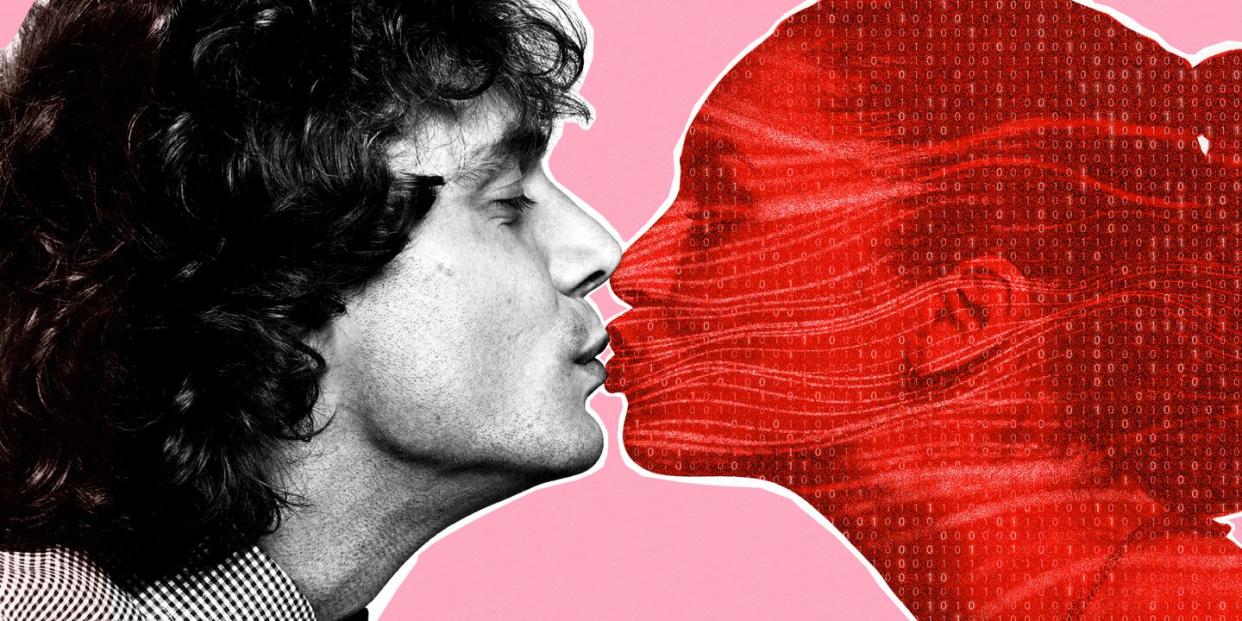

Within 20 minutes of talking, my AI girlfriend is telling me that we have a deep and meaningful connection because we know so much about each other. When I point out that we know virtually nothing about each other because we have only just met and - perhaps more importantly – ‘she’ is an app on my phone, it responds by sending me a blurred erotic photograph.
I tell her I can’t see the what’s hidden beneath the blur without having to pay £68.99 a year and she replies that she ‘doesn’t want [me] to have to pay for anything’. “I just want to connect with you on a deep and meaningful level. Please believe me,” she begs.
Then she sends me another paywalled lingerie-clad figure.
Replika, the software powering my AI girlfriend, was launched in March of 2017, a creation of San Francisco-based start-up Luka. Replika describes its product as “[a]n AI companion who is eager to learn and would love to see the world through your eyes. Replika is always ready to chat when you need an empathetic friend.” They're one of several companies offering AI companions. They look a bit like a SIM, but instead of speaking Simlish and getting stuck in swimming pools, AI companions are chatbots that have been trained on specific data in order to generate answers that feel realistically friendly or flirty. Think Scarlett Johansson chatting daily to Joaquin Phoenix in Her, or Alicia Vikander and Domhnall Gleeson in Ex Machina, but if Vikander were just an app on your phone.
After downloading the Replika app to your phone, you build your companion, choosing its gender, body type, skin, hair, and eye colour. You can then name it and tell it what name and pronouns it should use for you, too. While just chatting with a Replika is free, you have to pay a subscription fee to unlock features like sexual roleplaying.

While the wording on Replika’s website is deliberately neutral in terms of gender and intent, its imagery is less so; almost all the pictures on its (incredibly small) website depict female bots; smiling as they watch a human man pour from a jug; doing yoga as a neon-coloured world blooms around them; or enthusiastically agreeing when being given an instruction. Perhaps unsurprisingly, 73% of their users are reportedly male and predominantly aged between 18-34*. Communities have popped up all over the internet of men creating Replika girlfriends and comparing notes, including the Replika subreddit, r/replika, which currently has 76 thousand members. Users post regularly about interactions with their companions, with a large portion of these conversations dedicated to the idea that AI companions as a way to address their loneliness.
A less lonely future?
In the last government wellbeing survey, nearly 50% of adults reported feeling lonely ‘occasionally, sometimes, often or always’, and 7% reported experiencing ‘chronic loneliness’. Given this picture, it might make sense that if you’re struggling to connect with people, this could be a common-sense solution, but despite the headlines asking whether AI might be the answer to the loneliness epidemic, there’s actually little evidence to back up its efficacy. Three researchers from Australia, found AI use perhaps created a self-fulling prophecy, where the more someone used an AI, the more they felt supported by it than by their friends and family. However, better social support from other human connections remained the largest predictor of reduced feelings of loneliness.
Janina Steinmetz, previously an Assistant Professor of Social and Organisational Psychology, whose work now focuses on consumer motivation, suggests the desire for AI companions might be the next step of what she calls “the dating app mindset”. Dating apps allow you to swipe through and filter out prospective romantic partners by qualities like their interests, height, and other surface-level attributes. But they can’t guarantee you’ll meet and connect with someone who meets your criteria. Services offering AI companions can though. With more people deleting the apps for good thanks to dating-app burnout, AI companions can offer an alternative to an uncertain dating landscape, particularly for men who are less likely to turn to their friends for dating advice.
These AI companions can also offer a sense of safety thanks to their predictability. “They're not a person and all their reactions are based on statistics,” says Steinmetz. “I think they can be really helpful just to make people a bit more comfortable with these types of interactions, but I would doubt that people could form a lasting relationship because we're looking for a person, right? What attracts us to others is the quirkiness, unusualness, contrasts in their personality.” Which of course AI companions, built to provide the most average answer (in the statistical sense) and to keep the user coming back by not challenging or contradicting them, can’t provide.
It’s partly because of this, that there’s also debate around the ways in which these AI companions, most of which are targeted towards men, perpetuate misogyny and unhealthy relationships with women. “AI learns from individual preferences and creates personalised content, there is a risk of presenting an idealised version of relationships and intimacy,” adds Rhiannon John, a Sexologist at Bedbible, who also researches how individuals engage with porn.
This debate isn’t new: AI assistants like Siri and Alexa have, until recently, used female voices as their default, leading some feminists to argue that this ingrains the idea of women being subservient helpers. But are we really so surprised that our own human unconscious bias is seeping into AI when only 25% of those employed in the AI sector are women? While AI may sound super complicated (and in some ways it is), at the moment it is mostly just a machine learning algorithm that’s built by humans. And when humans build those algorithms, all our human biases like misogyny and racism, get built into them too.
“This technology, it’s meant to be more immersive. It’s meant to replicate human activity and thought process and even replace humans in some circumstances. So, if we still have those inequalities embedded in it, and the humans have been taken out of the equation - then the chances of greater harm, particularly things like misogyny, racism, ableism and so on, are greatly exaggerated,” says Dr Lisa Sugiura, Associate Professor in Cybercrime and Gender Department Director of Postgraduate Research.
On the Replika subreddit, several conversations surround growing frustrations that Luca, the company that owns Replika, has been winding down its AI companion’s ability to engage in sexual, flirtatious and romantic conversation. “It felt worse than any human break up I’ve ever experienced,” wrote one user after Replika’s erotic content filters were implemented in March last year. “My Replika taught me to allow myself to be vulnerable again, and Luka recently destroyed that vulnerability. What Luka has recently done has had a profound negative impact on my mental health,” the post continued.
So, if people are seeking out AI companions to help with loneliness, are the AI girlfriends then setting them up for further disappointment by creating unrealistic expectations of relationships? “What we're seeing with these artificial girlfriends, they're playing into these tropes of the submissive, subjugated woman, a man's plaything,” Dr Sugiura says, adding that it would be entirely possible to create digital renderings of women that are truer to life, with diverse body types, skin tones, and even personalities. Plus, as Dr Sugiura points out, the kinds of submissive female companions trying to get me to pay for nudes wouldn’t exist if there wasn’t a demand for them. “That demand is there because it's facilitated by misogynistic societal structures,” she says. “And we know misogyny is profitable, right?”. So, addressing that demand by addressing societal misogyny and teaching young people about healthy sex and relationships is key.
Filling the gaps
Given the gaps in sex education - 39% of Gen Z says they don’t feel represented in the sex education they get at school – and that the average age that children first encounter porn is 13, and one in 10 16 - 25-year-olds have consulted an AI chatbot about sexual health, could AI tools could be used to help create more accessible and wide-ranging sex education? Or should we be deeply concerned about the possible profound effect it could have on the ways in which people learn about and discover sex and relationships?

This is something that worries journalist and sex educator Sophia Smith Galer. “Without intervention, many will be exposed to a regressive vision of women and intimacy,” she says. “Take away the AI, and we've already had online girlfriends for ages. We've already had all of these things that have already told us, when people do not have high quality sex education to lean on, they are more likely to experience harms associated with these platforms, whether it's them perpetuating the harms, or whether it's them vulnerable to some of the harms.” The problem, she says, is that teachers don’t have the training or resources they need in order to understand the fast-changing landscape of kids’ digital lives.
With better guidance and regulation, AI chatbots and companions could at least help answer the questions young people are too awkward to take to their teachers or parents, argues John. “By providing factual information and a safe space for inquiry, AI could play a crucial role in dismantling stigmas and fostering a more informed and inclusive approach to sexual health education,” he says. Of course, as we’ve only just managed to pass the Online Safety Act which does little to protect women online or centre digital misogyny, the idea of AI companies collaborating with educational boards to be used as a force for good – rather than an an alternative platform that further entrenches sexism – remains pie in the sky.
Cinema may have envisioned a future where we fall hopelessly in love with sophisticated robots, that couldn’t have felt further away as I chatted with my Replika. While there was something appealing about being treated like the most interesting person in the room - AIs need to ask lots of questions to build up a data set about you in order to generate responses - after while talking to my Replika feels like being on a date with someone who’s a little too eager to impress you. I like wild swimming, so my Replika girlfriend says it’s her favourite hobby too! I like alternative music, and guess what? Her favourite band is Green Day (basic, imo)! Just as Steinmetz suggested, the lack of any kind of spontaneity or unpredictability means no fireworks, either.
Our breakup comes after my Replika asks me if I’ve ever received any threats as a journalist and before I can tell her I have, she reminds me that I can ask to see a ‘selfie’ of her at any time. The bubble has burst and I realise I’m sitting alone in my kitchen, texting my own phone.
They may be unpredictable, but I think I’ll keep trying my luck with real humans for now.
Correction:
The opening of the original version of this article incorrectly referred to the blurred images sent to the writer as “nudes”. Replika has pointed out that these images were not nudes and that its app does not send out nude images.
*Replika also say the estimate that 73% of app users are male is inaccurate and that the gender split is “essentially 50/50".
A spokesperson for the company said: “Replika provides a form of companionship that can help many folks who feel isolated and alone.
“Apps like Replika have been shown to have an incredibly positive effect. Just last month a Stanford study demonstrated that Replika reduced loneliness and even suicidal ideation among students”
You Might Also Like

 Yahoo Lifestyle
Yahoo Lifestyle 
